One of the most exciting advancements in modern medicine is robotic surgery—a form of minimally invasive surgery that allows for greater precision, faster recovery, and improved outcomes for patients.
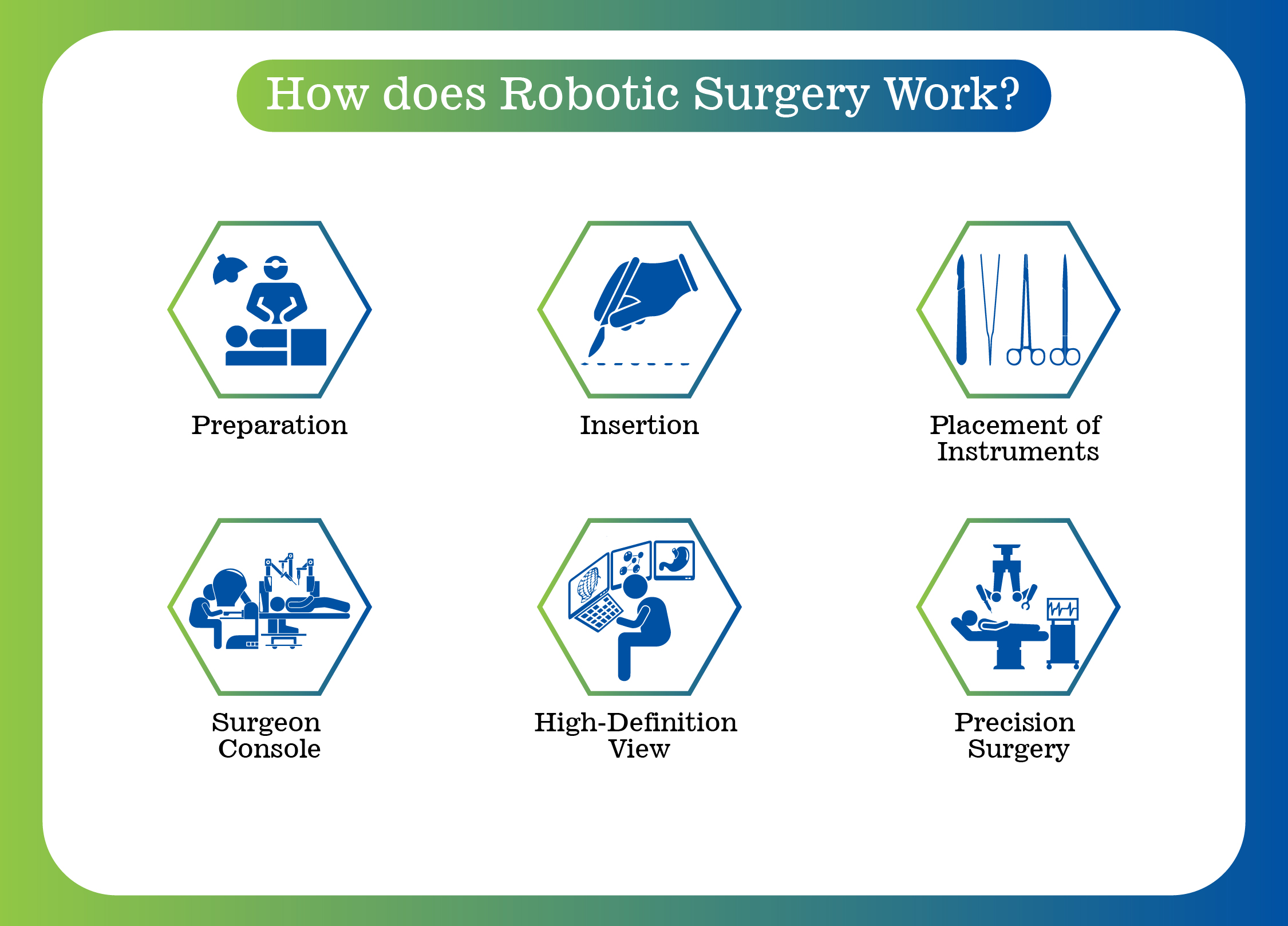
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, is a type of minimally invasive procedure where surgeons use a robotic system to assist with the operation. Instead of making large cuts as in traditional open surgery, robotic surgery uses tiny incisions through which miniature instruments and a high- definition camera are inserted.
The surgeon controls the robotic arms from a specialized console. These robotic arms move with greater precision than the human hand, allowing for delicate procedures to be performed with minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
Importantly, robotic surgery is not performed by a robot independently. The surgeon remains in full control of the system at all times. The robot does not make decisions or act on its own; it simply serves as a highly advanced tool that enhances the surgeon’s ability to perform complex tasks.
Robotic surgery typically uses a surgical platform like the da Vinci Surgical System, one of the most widely used robotic systems in the world:
This level of control enables more precise movements, minimal bleeding, reduced trauma, and quicker recovery.
Robotic surgery is widely used across multiple medical specialties:
These procedures benefit from robotic precision, reducing nerve damage risk and preserving urinary and sexual function.
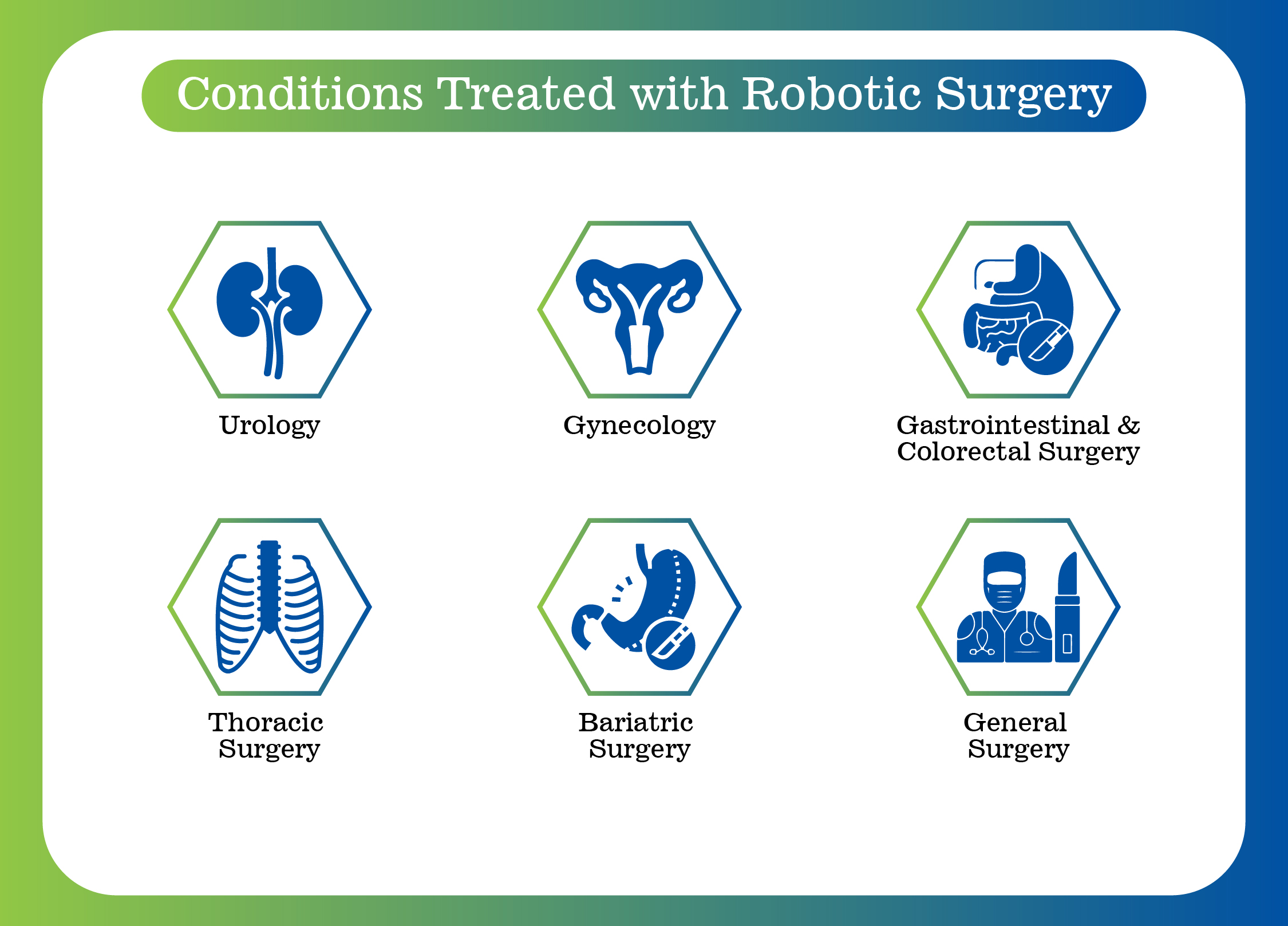
These procedures often result in less blood loss, fewer infections, and faster recovery.
These procedures benefit from robotic precision, reducing nerve damage risk and preserving urinary and sexual function.
The robotic approach allows greater control in the confined space of the chest, minimizing the need for large incisions.
Here’s why robotic surgery is increasingly preferred by both doctors and patients:
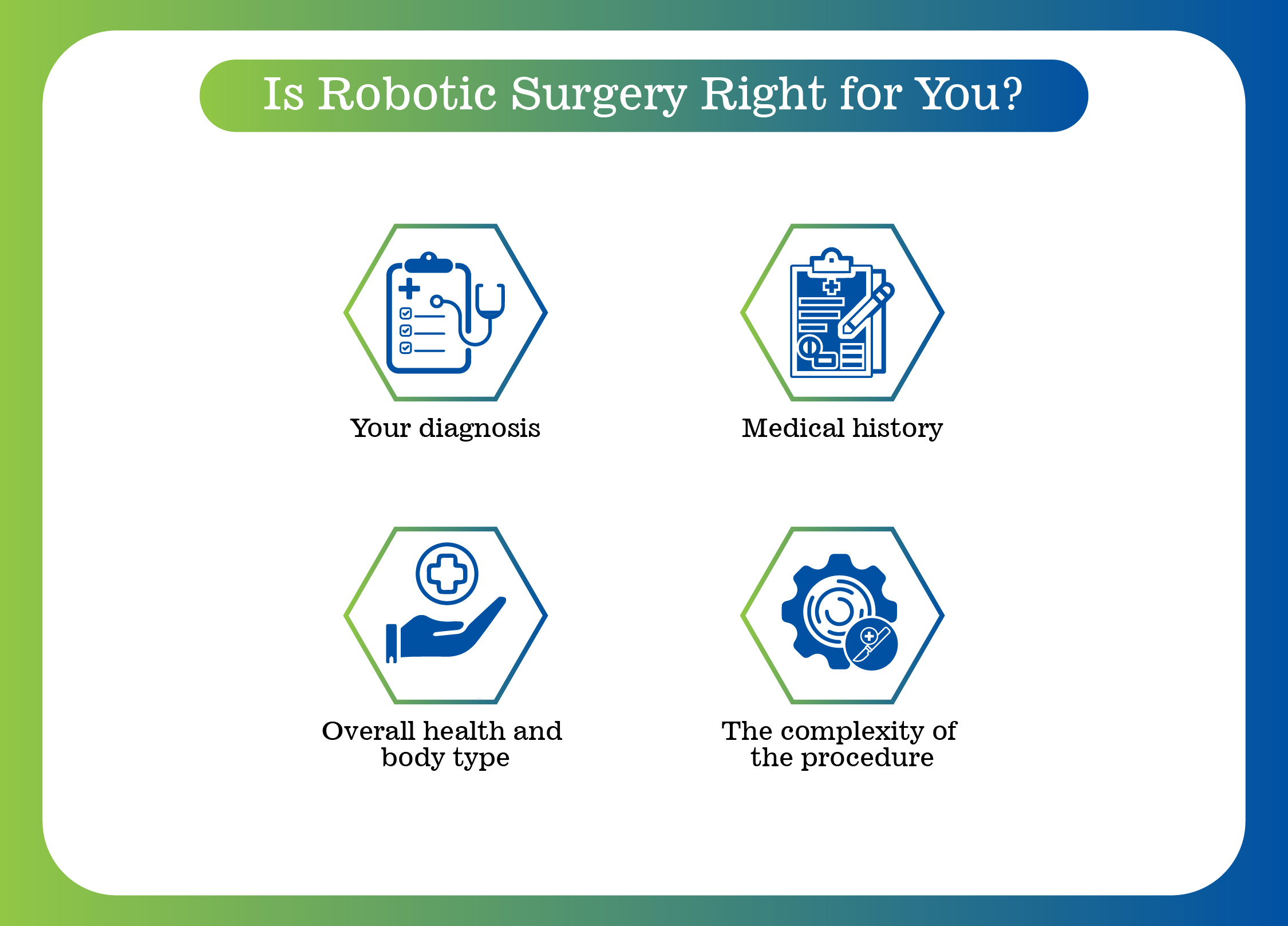
While robotic surgery is a great option for many procedures, it's not suitable for everyone. Your doctor will assess:
We’ll help you understand all options, including the risks and benefits, so you can make an informed decision.